The perfect combination for healthy growth
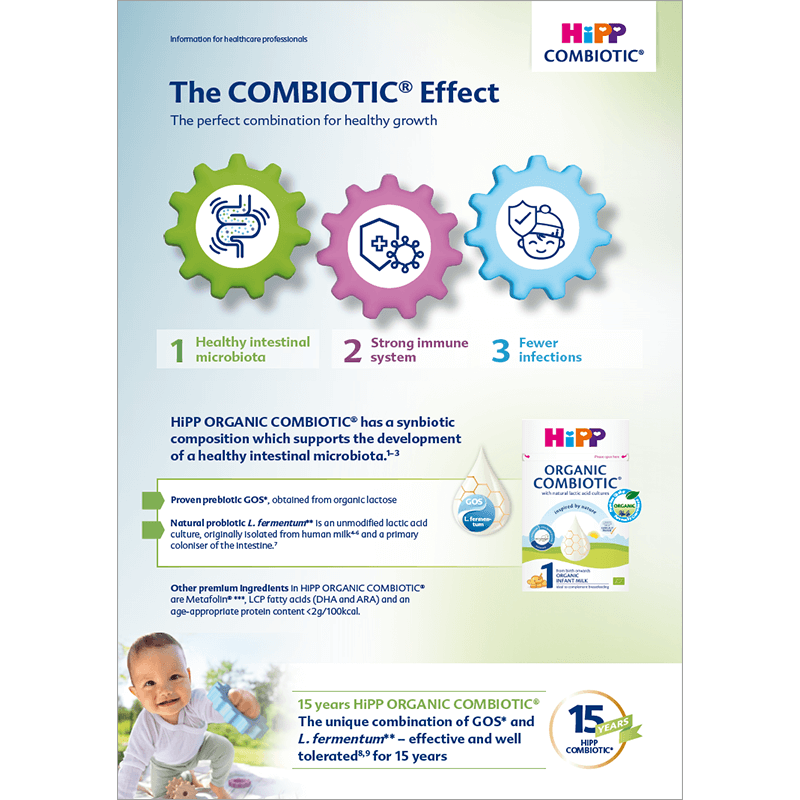
The COMBIOTIC® Effect
The perfect combination for healthy growth
HiPP ORGANIC COMBIOTIC® contains prebiotic galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS) and probiotic lactic acid cultures (Limosilactobacillus fermentum ECT 5716). This synbiotic approach promotes a healthy intestinal microbiota, leading to a strengthened immune system and subsequently fewer gastrointestinal and respiratory infections.
This "effect cascade" of healthy gut microbiota → strong immune system → fewer infections is referred to as the COMBIOTIC® Effect.
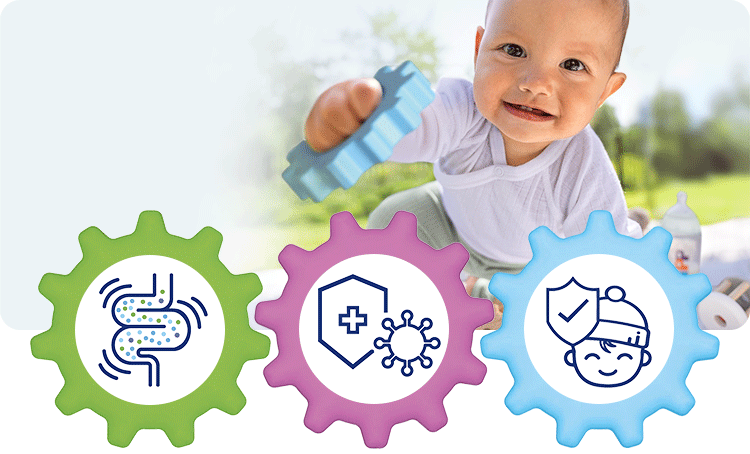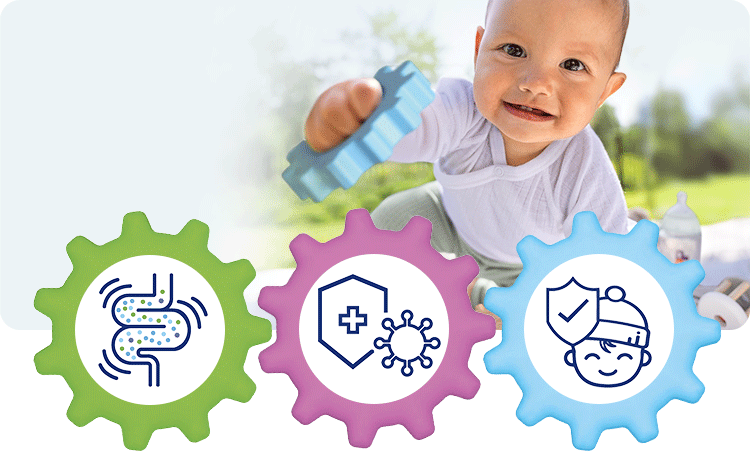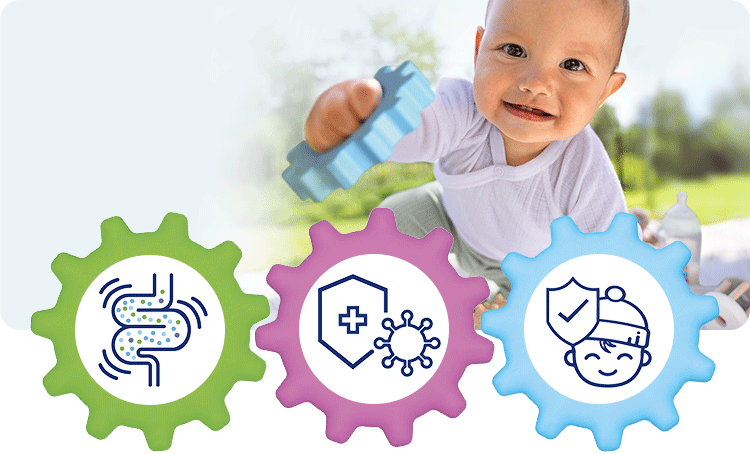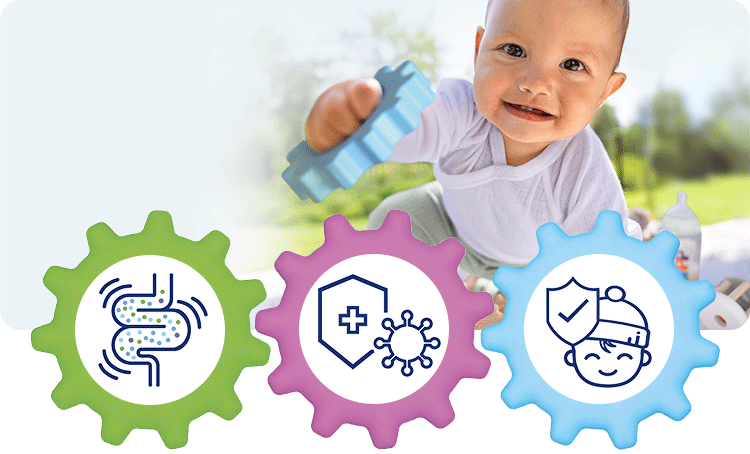
1. Healthy intestinal microbiota
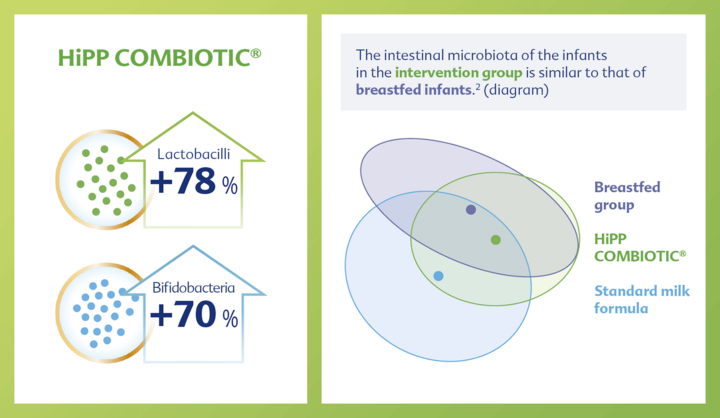
With GOS and L. fermentum –> increased colonisation of the intestine with bifidobacteria (+70%) and lactobacilli (78%)1 –> intestinal microbiota more similar to that of breastfed infants.2
2. Strong immune system
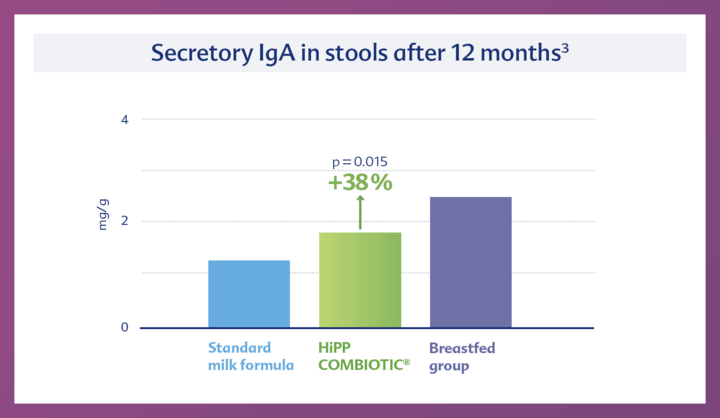
Secretory IgA in stools, a marker for the intestinal immune system, is increased by 38% after 12 months in comparison to the control group.3
3. Fewer infections
Cases of diarrhoea1,4 and respiratory infections1,3 were significantly reduced. These effects were demonstrated in the GOLF studies.

Part 1: Healthy intestinal microbiota
The development of gut microbiota is crucial from the very beginning, as approximately 80% of immune-competent cells are located in the gut. HiPP ORGANIC COMBIOTIC® promotes increased colonization of the gut with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli1 through the prebiotics and probiotics GOS and L. fermentum. This results in an intestinal microbiota similar to that of breastfed infants.2
Part 2: Strong Immune System
It is known that a young, still immature immune system requires stimulation from the gut microbiota and is essentially "trained" by it. This maturation process is supported by the components of human milk. HiPP ORGANIC COMBIOTIC® leads to a similar effect in non-breastfed children. A study demonstrated the strengthening of the immune system, shown by a significantly increased secretory IgA in stool by 38% compared to standard formula.3

Part 3: Fewer Infections
The GOLF studies have demonstrated the clinical benefits of HiPP ORGANIC COMBIOTIC®. In GOLF I, the intervention formula was COMBIOTIC® follow-on formula, and the number of upper respiratory infections was significantly reduced by 26%, while gastrointestinal infections were reduced by 46%.1
GOLF II examined the use of COMBIOTIC® infant formula, showing an even greater effect on gastrointestinal infections, with a significant reduction of 71%.4
The current study – GOLF III – investigated both infant and follow-on formulas. Here, the number of lower respiratory infections was significantly reduced by 23%, with the incidence being at the level of the breastfeeding group.3
HiPP COMBIOTIC® - Not only clinically effective, but also well tolerated
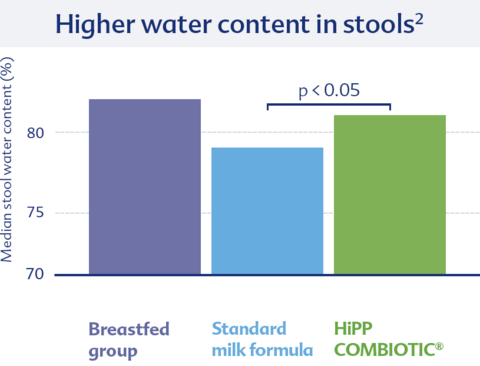
In addition to clinical benefits, it is essential for infant formula to be well tolerated by children. For example, it has been shown that the water content in the stool of the COMBIOTIC® group was significantly higher compared to the standard group and comparable to that of breastfed infants.2
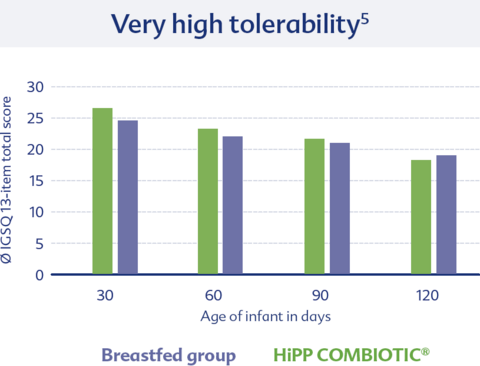
Another study examined tolerability using a standardized questionnaire (IGSQ). HiPP ORGANIC COMBIOTIC® showed again very good tolerability, similar to that of breastfed infants.5
Science and Nature Hand in Hand
With HiPP ORGANIC COMBIOTIC®, HiPP demonstrates its guiding principle "Science and Nature Hand in Hand": a scientifically based concept with ingredients largely derived from nature, continuously developed with leading experts in nutritional research.
- Many years ago, the protein content was reduced to below 2g/100kcal according to current findings to minimize the risk of obesity.
- Long-chain fatty acid DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) was used long before it became legally required, and HiPP voluntarily adds ARA (arachidonic acid) to its infant formulas.
- Since 2021, Metafolin®* - the natural form of folate found in human milk - has complemented HiPP ORGANIC COMBIOTIC®.
Suitable HiPP info material
References:
1 Maldonado J et al. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 2012; 54(1): 55–61.
2 Lagkouvardos I et al. Am J Clin Nutr 2023; 117 (2): 326–339.
3 Piloquet et al. Am J Clin Nutr 2024; 119(5):1259–1269.
4 Gil-Campos M et al. Pharmacol Res 2012; 65(2): 231-238.
5 Otten et al. Nutrients 2023; 15:4674.
6 Riley A.W. et al. Clin. Pediatr. 2015;54:1167–1174.
*Metafolin® is a registered trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany.


