05.2023
Author Dr. J. Hower, Paediatrician from Germany
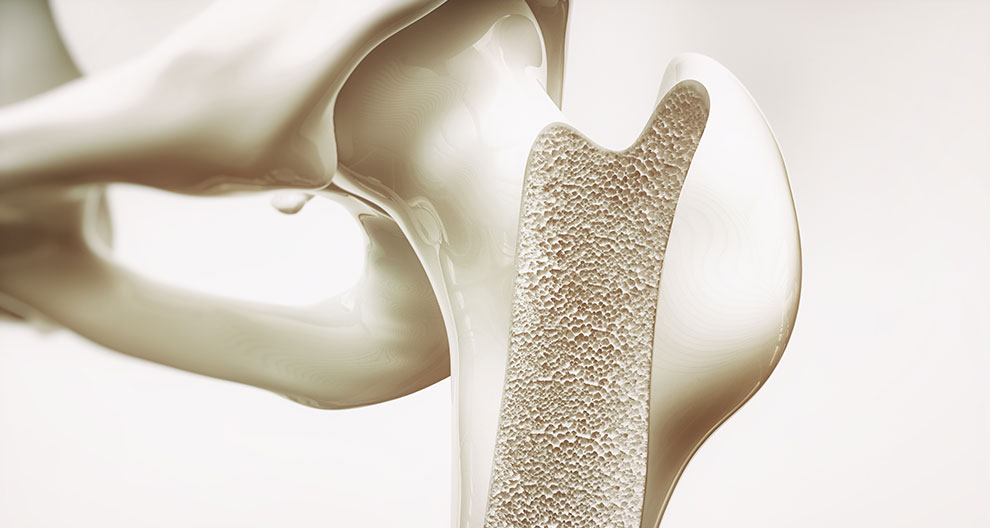
There is strong evidence that inadequate intake of certain micronutrients and macronutrients can affect bone health. It is unclear, however, whether a purely plant-based diet leads to poorer bone health. The authors have conducted a review of current findings on this topic.
A purely plant-based diet is gaining increasing public interest as it can improve metabolic health. Studies that examine vegetarians and vegans together show a lower bone mineral density (BMD) but not always an increased fracture risk compared to omnivores. However, vegans consistently have a higher risk of fracture, especially at the hip. The higher risk of fracture may be due to reduced intake of calcium and vitamin D, as well as the quantity and quality of proteins in the diet. Other nutrients (B vitamins, selenium, zinc, iron, iodine) or physiological factors (lower body mass index, microbiome, or endocrine profile) may also play a role, but have not yet been studied in detail.